Consideration of climatic factors within Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA)
Guidance on the consideration of climatic factors within Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA), developed by the Scottish Environmental Protection Agency (SEPA).
3. SCOTLAND'S GREENHOUSE GAS EMISSIONS
3.1 In Scotland in 2007, approximately 61.3 million tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalents (Mt CO 2e) were emitted. Figure 2 below shows the sources of these emissions. It is important to note that forestry and other land uses can absorb some emissions. This reduced Scotland's overall emissions by 4.4 Mt CO 2e, meaning Scotland's net carbon dioxide equivalent emissions for 2007 were 56.9 Mt CO 2e. 2
3.2 Scotland accounts for approximately 0.15% of global greenhouse gas emissions due to human activities. As Scotland only has around 0.08% of the world's population - we produce far greater level of emissions than the average, when considered in proportion to our population size. In 2007, Scotland's net greenhouse gas emissions were made up of around 80% carbon dioxide emissions and 20% of the other five greenhouse gases.
3.3 Scotland's bogs, wetland and upland systems act as a vital "carbon bank". Scotland's organic soils hold 10,028 Mt CO 2e 3 , this compares with a total of 418 Mt CO 2e in UK surface vegetation 4 . To put this into context, Scotland's net 2007 greenhouse gas emissions equate to around 0.6% of Scotland's total soil carbon bank.
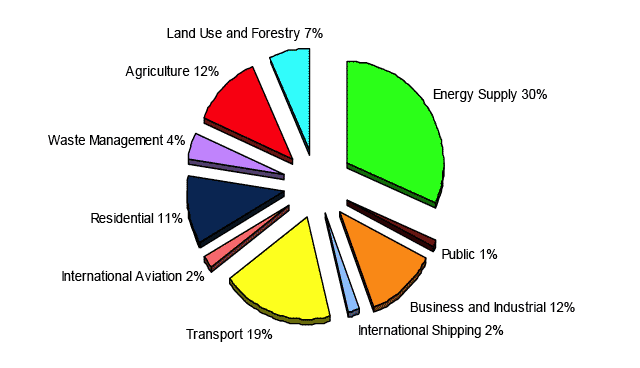
Figure 2 - Sources of Scottish Greenhouse Gases by sector, 2007 5
There is a problem
Thanks for your feedback